Software

The Sentinel-1 interferometry processor is developed by the Radar Imaging Geodesy Group at Peking University. The software package is designed for large-scale InSAR processing with Sentinel-1 TOPS images, which includes 4 modules:
Key features include.
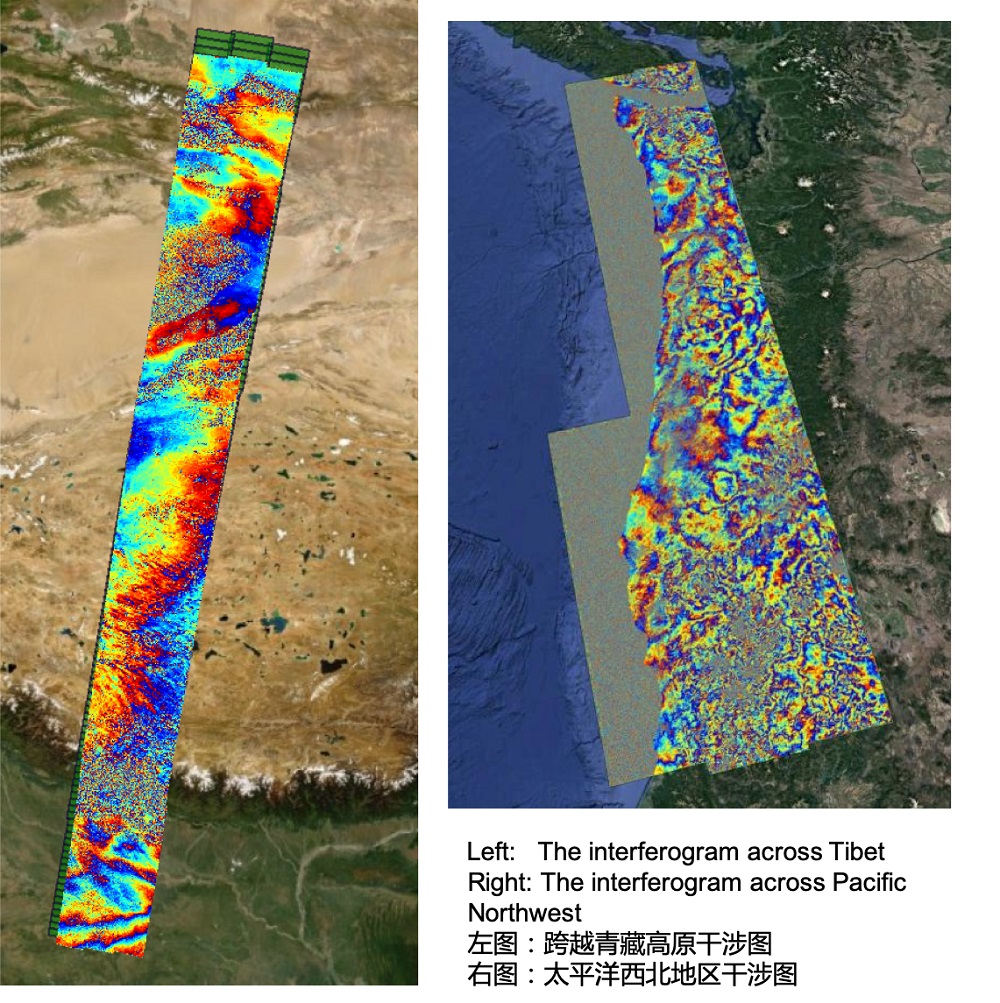
The processing is based on Sentinel-1’s burst configuration, allowing for flexible processing strategy. The mosaic of burst interferogram is unlimited. The software can not only process single-burst interferogram, but also mosaic any number of frames to form an interferogram spanning thousands of kilometers.
The software is fully parallelized based on multi-thread algorithms. The processing time for producing one full-frame geocoded interferogram (90m resolution) is only 5 minutes and 5 seconds (test environment: Thinkpad Laptop, Intel(R) 6-core i7-8850H CPU @2.60GHz, 32 GB RAM, SSD hard drive).
The entire process is fully automatized. According to the application requirements, users only need to set the multilook factors, filter parameters, baseline thresholds for interferometric configuration and a few parameters regarding to the area of interest. After that, the data processing can be done without human interaction.
The software uses a de-reference SLC storage strategy, which allows for less storage space occupation, fast and flexible processing. Users can quickly generate any interferograms based on given baseline configuration. After the burst-based processing, the processing time for producing a geocoded full-frame interferogram (90 meters) is less than one minute.
Interferograms are stored in geotiff format, and the radar parameter files are stored in text files. Users can choose any area in the map interface to export the result to StaMPS format for time-series InSAR analysis.
Windows graphical user interface, easy to operate, easy to use, no professional training is required to generate interferograms for various applications.

Sentinel-1 干涉处理器是北京大学雷达影像测地学团队针对Sentinel-1 TOPS数据开发的广域InSAR数据处理软件。包含四大模块:
主要特点包括:
数据处理基于Burst进行,更加灵活可控。拼接无限制,既可以处理单个burst,也可以拼接任意多frame的数据,形成数千公里长的干涉图。
采用CPU多线程并行算法,干涉处理速度快于市面上所有哨兵1号SAR数据处理软件,处理一个标准副干涉影像对,从影像配准到地理编码干涉图(90米分辨率)5分5秒(测试环境为Thinkpad笔记本电脑,Intel(R) 6核i7-8850H CPU @ 2.60GHz,32 GB内存,SSD硬盘)。
整个处理过程基本全自动化进行。只需根据应用需求设置多视、滤波等参数,其他数据处理参数无需人为干预。
采用去参考相位SLC存储策略,一次配准后即可快速生成任意基线组合干涉图(90米分辨率干涉图小于一分钟一对),存储空间占用少,干涉处理快速、灵活。
干涉图为通用geotif格式存储,雷达参数文件以文本方式存储。可在地图界面选择任意区域将结果导出为StaMPS处理格式进行时序处理。
Windows系统下专业图形界面,操作方便、易于上手,无需专业培训即可生成各种应用场景下的干涉图。
Click to download
If you’d like to use the trail version (can process images acquired in 2019 and 2020) for teaching, much appreciate if you could let us know your affiliation and some basic information about your class. Feedbacks from you and your students will help us improve the software.
Manual
LICSBAS for Windows
Forked from the original LICSBAS and revised the code to support running on windows. See revised source code
LiCSBAS is an open-source package in Python and bash to carry out InSAR time series analysis using LiCSAR products (i.e., unwrapped interferograms and coherence) which are freely available on the COMET-LiCS web portal.
Users can easily derive the time series and velocity of the displacement if sufficient LiCSAR products are available in the area of interest. LiCSBAS also contains visualization tools to interactively display the time series of displacement to help investigation and interpretation of the results.
Interferogram Simulator
This code provides a dataset simulation method that can provide training samples with strong generalization ability for model training. Deep learning, as a data-driven method, requires a large number of training samples to train network models. However, it is difficult or even impossible to obtain ground truth corresponding to InSAR data because it is difficult to collect high-resolution ground deformation information, which limits the application of deep learning in the field of InSAR. We study the phase characteristics of a large number of real interferograms, analyze the statistical models of InSAR data and noise sources, and propose a strategy to construct training samples by simulating the phase components of terrain, buildings, deformation, atmosphere, water surface and noise separately, which is applicable to training networks for different tasks such as interferogram denoising, deformation detection and phase unwrapping. Experimental results show that this dataset simulation method can effectively train deep network models with good generalization ability on real data.
